How Do I Use Technical Analysis to Trade?
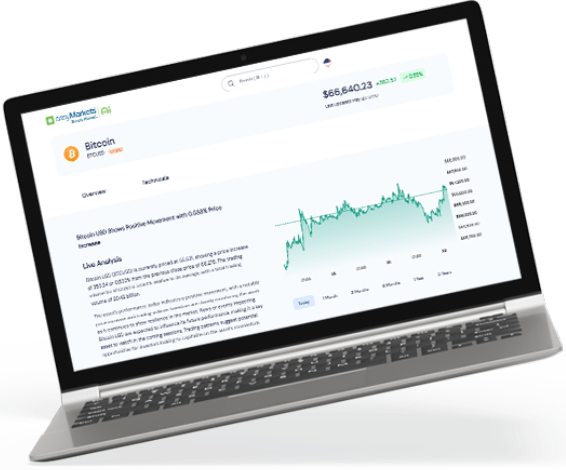
If you’ve ever seen a forex chart with a lot of lines and waves, then that’s technical analysis being applied in gauging where price could go next. The concept behind technical analysis is that past price action may repeat itself so traders try to observe price patterns in predicting future moves.
Various Analytical Tools Available
There are various tools that can be used to conduct technical analysis. Among these are inflection points, Japanese candlestick formations, chart patterns, and technical indicators.
Inflection points are perhaps the easiest to grasp and apply among the technical analysis tools. This may comprise support and resistance, wherein the former indicates a level at which price may bounce higher from and the latter indicates a level at which price may fall lower from. Support and resistance may be determined by looking at past price action, watching psychological levels (00s and 50s), or applying formulas that generate potential support and resistance areas.
Also included under inflection points are trend lines, which connect the recent highs of price action in a downtrend and the latest lows of price action in an uptrend. Ascending or descending channels can also be drawn by connecting parallel highs and lows. Fibonacci retracement and extension tools can also be used as inflection points to see where price may pull back in an ongoing trend.


Japanese candlestick analysis compares the open, high, low, and close of price action in a particular period of time and can be conducted on individual candles or a group. This may involve a lot of memory work in terms of recognizing the patterns, but this technical analysis tool has been applied for a long period of time and is still being watched by majority of traders.
Chart patterns are also reliable tools for technical analysis and may be easier to remember because of their names compared to Japanese candlesticks. There’s the double top and double bottom, the head and shoulders and the inverse head and shoulders, the bullish and bearish flag, the ascending, descending, and symmetrical triangle, the cup and handle, and so on.
Lastly, technical indicators comprise the likes of moving averages, stochastic, RSI, parabolic SAR, Bollinger bands, MACD, and volume indicators. These have complex mathematical formulas and rationale behind their calculations but it’s only important to understand how they function and how signals are generated.
For instance, moving averages usually incorporate the average closing prices for a specified period of time. A declining moving average means that the currency pair has been continuously moving lower, hinting that further declines may be in the cards. These indicators can be used on a singular basis or in combination with other moving averages of different parameters.
These technical indicators can be grouped into leading and lagging indicators. As their name suggests, leading indicators give a signal before a trend might change while lagging indicators simply confirm ongoing trends. Leading indicators may be prone to giving false signals since they occur early on while lagging indicators may give late signals, which is why it’s generally recommended to watch one leading indicator in tandem with a lagging indicator. A list of these indicators can be found in the easyMarkets Learn Center.